ERMI: Environmental Relative Moldiness Index
What Is ERMI?
ERMI is the Environmental Relative Moldiness Index – the combination of EPA research, powerful PCR technology, and a new method to screen homes for mold.
Based on recently published data from EPA researchers and the 2006 HUD American Healthy Home Survey, the test has been developed as a tool to evaluate the potential risk of indoor mold growth and associated health effects.
How Does ERMI Work?
The ERMI test involves the analysis of a single sample of dust from a home. The sample is analyzed using mold-specific quantitative polymerase chain reaction (MSQPCR), a highly specific DNA-based method for quantifying mold species. A simple algorithm is used to calculate a ratio of water damage-related species to common indoor molds and the resulting score is called the Environmental Relative Moldiness Index or ERMI.
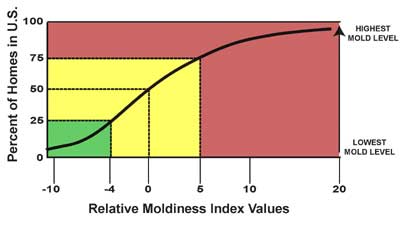
How Was ERMI Developed?
In initial studies by the EPA, the concentrations of different mold species in “moldy homes” (homes with visible mold growth or a history of water damage) and “reference homes” (homes with no visible mold) were compared. Based on those results, mold species were selected and grouped into those with higher concentrations in moldy homes (group 1) and those with lower concentrations (group 2). .
What Are The Advantages of ERMI Testing?
The ERMI offers several advantages over traditional mold screening methods. Carpet dust acts as a reservoir for mold spores and is more representative of mold levels over time versus short-term air samples. The use of MSQPCR for this test allows for increased precision as it is based on a biochemical assay using calibrated instrumentation. Further research is being conducted and published that will link the ERMI assessing health risks for susceptible individuals This information along with the national database will be invaluable in providing an objective and standardized method for screening homes for mold.

Recent Comments